So, you're wondering how fast an electric bike can really go? The answer isn't as simple as a single number. For most e-bikes in Australia, the motor assistance is legally capped at 25 km/h (around 15.5 mph) when powered solely by the motor, though pedal-assist can go faster. Hop over to the US, though, and you'll find bikes that can assist you all the way up to 28 mph (45 km/h), depending on the bike's classification. Right off the bat, you can see that where you live is a huge factor.
How Fast You Can Really Expect Your E-Bike To Go
The speed you see advertised on the box often tells only half the story. While a bike's motor might be capable of hitting some pretty high speeds, the legal limit is what really dictates how fast it will help you go. It's kind of like the difference between a car's top speed on a racetrack and the speed limit you have to obey in a school zone.
This is where the e-bike classification system becomes super important. Different regions have set up specific rules to define what counts as an "electric bike" and how fast it can legally move on public roads. Getting a handle on these classes is the first step to understanding what your real-world speed will look like.
Understanding E-Bike Classifications
In the United States, e-bikes are usually sorted into three distinct classes. These categories determine the maximum assisted speed and whether the bike comes with a throttle. Australia, on the other hand, has a more unified national standard for what they call a 'pedalec', though specific state rules can vary.
Here’s a quick rundown of what these classes mean for your ride:
- US Class 1: The motor only kicks in when you're pedaling, and it cuts off once you hit 20 mph.
- US Class 2: This class comes with a throttle that can power the bike up to 20 mph, even if you're not pedaling.
- US Class 3: This is pedal-assist only (no throttle), but with a higher speed limit where the motor helps you up to 28 mph.
- Australia (Pedalec): The motor provides assistance up to 25 km/h (15.5 mph). Throttles are generally not permitted for bikes to be classed as standard bicycles.
This image really drives home the main difference in speed limits between Australia and the US.
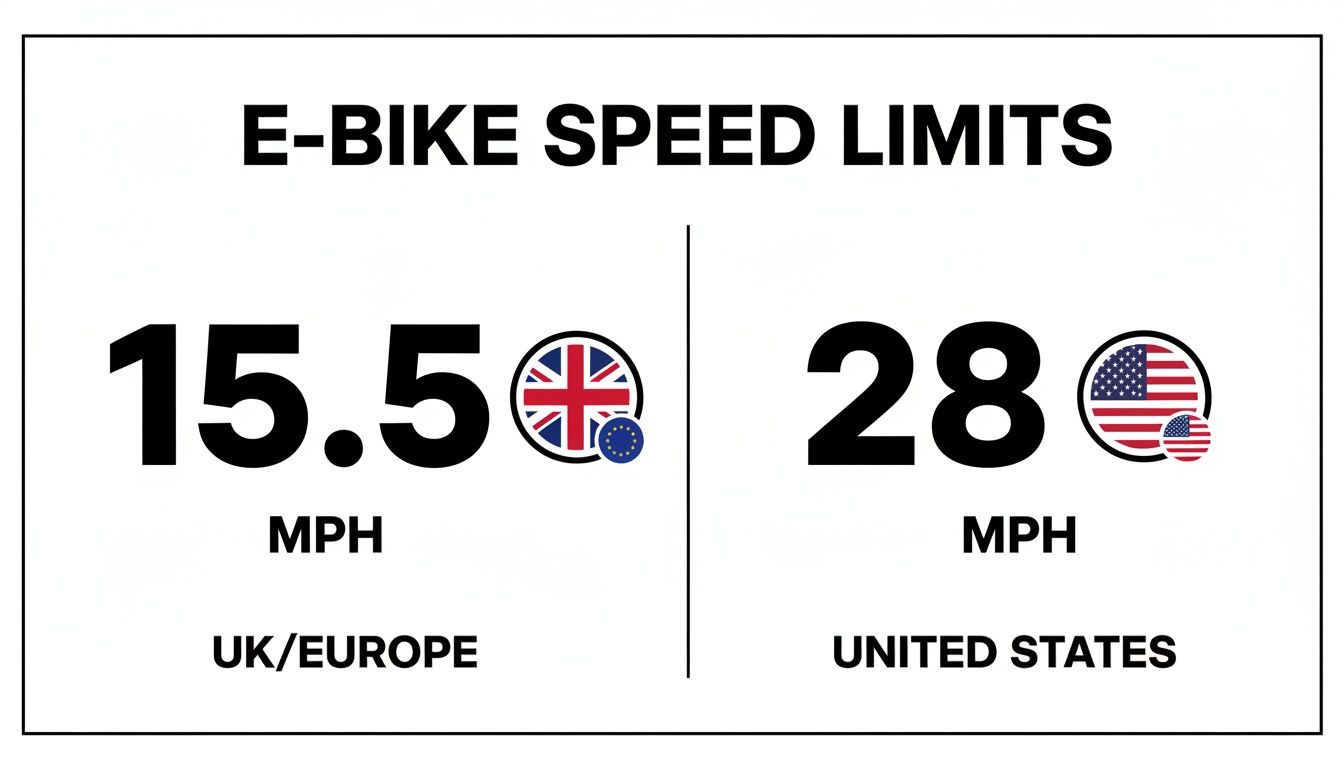
The biggest takeaway here is that riders in the US on a Class 3 bike can legally zip along with motor assistance much faster than their Australian counterparts.
E-Bike Classes And Speed Limits At A Glance (AU & US)
To make things even clearer, let's break down the legal speed limits and rules for the main e-bike classifications across these major regions. This table gives you a quick side-by-side comparison.
| Region / Class | Assist Speed Limit | Throttle Allowed? | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia (Pedalec) | 25 km/h (15.5 mph) | No, pedal-assist only | City commuting, leisure riding, bike paths |
| US Class 1 | 20 mph (32 km/h) | No, pedal-assist only | Bike paths, trails, general commuting |
| US Class 2 | 20 mph (32 km/h) | Yes, up to 20 mph | Casual rides, accessibility, effortless cruising |
| US Class 3 | 28 mph (45 km/h) | No, pedal-assist only (usually requires helmet) | Fast commuting, keeping up with urban traffic flow |
As you can see, the US system offers a lot more variety, especially for riders looking for higher speeds for their daily commute. The 28 mph cap for Class 3 bikes is a game-changer for people wanting to replace car trips.
It's crucial to remember the difference between what a bike can do and what it's legally allowed to do. While many e-bikes could technically go faster, they are governed to stay within these limits. You can find more great insights into e-bike speed regulations over at Leoguarbikes.com.
Understanding The E-Bike Speed Laws That Matter

Before you try to max out your e-bike's speedometer, it's crucial to understand the rules of the road. Think of e-bike laws as the official playbook for sharing the streets safely. Ignoring them doesn't just risk a fine—it puts you and everyone around you in a potentially dangerous spot.
These regulations aren't one-size-fits-all, either. What’s perfectly legal for a rider cruising in California could be off-limits for someone zipping through the streets of Sydney. Let's break down the key differences you need to know.
The Australian Standard: The Pedalec Framework
Down Under, things are pretty clear-cut on a national level. For an e-bike to be treated just like a regular bicycle (meaning no license or registration), it has to be a ‘Pedalec’.
To qualify as a Pedalec, an e-bike must follow two golden rules:
- Motor Power: The motor can’t have a continuous power output of more than 250 watts.
- Assisted Speed Limit: The motor has to stop helping you once you hit 25 km/h (15.5 mph). You can definitely pedal faster on your own steam, but the motor cuts out at that specific speed.
A key feature of a Pedalec is that it must be pedal-assist only. That means no "twist-and-go" throttle that works without you pedaling. The whole point is that you're still cycling, just with an electric boost.
This simple framework keeps e-bikes in the same category as traditional bikes, making it easy to know where you can and can't ride. If a bike has more power or speed, it’s usually considered a motor vehicle and comes with a whole different set of legal requirements.
The US Class System: A Different Approach
The United States takes a more flexible approach with a tiered classification system that gives riders more choice, especially when it comes to speed. While there's a basic federal definition, most states have adopted a three-class system. It’s why you’ll see e-bikes in the US clearly labeled as "Class 1," "Class 2," or "Class 3."
Here’s a quick rundown of what those classes mean for you:
- Class 1: This is a pedal-assist-only bike. The motor helps you out as you pedal, but it cuts off once you reach 20 mph. These are generally allowed wherever you can ride a standard bicycle.
- Class 2: These e-bikes come with a throttle. You can push a button or twist a grip to get moving up to 20 mph without even pedaling. Of course, they also have a pedal-assist mode that caps out at the same speed.
- Class 3: These are the speedsters of the legal e-bike world. They are pedal-assist only (no throttle allowed) and will keep helping you all the way up to 28 mph. Because they're faster, they often come with stricter rules, like age limits and helmet requirements.
This system gives American riders a great range of options, from laid-back beach cruisers to zippy commuters that can keep up with city traffic. But since the specific rules can change from state to state or even city to city, it's always smart to check your local laws. For a complete overview, check out our guide to electric bike laws by state.
Following the law is about more than just avoiding a ticket—it's about being a responsible rider. Understanding the rules helps keep everyone safe, but it's also wise to know what to do if an accident happens. If you're ever in an unfortunate incident, knowing your options, including seeking personal injury legal services, is just part of being prepared. At the end of the day, riding within the legal limits is all about contributing to a safer, more enjoyable cycling culture for all of us.
What Actually Powers Your E-Bike Speed
Ever wondered what separates a zippy e-bike that leaps off the line from one that feels more like a gentle cruiser? It’s not magic—it's the tech humming away inside the frame. To really get a grip on how fast an electric bike can go, we need to pop the hood and look at what's delivering the juice.
Think of it like cars. A little city runabout and a big V8 truck are totally different beasts, even if they're stuck in the same traffic jam. It’s the same deal with e-bikes, and it all starts with the motor.
Motor Power (Watts)
The first number you’ll almost always see is motor power, measured in watts (W). Simply put, watts are like the horsepower rating for your bike. More watts generally means more raw power.
In Australia, legal e-bikes are capped at a continuous power output of 250W. But over in the US, things get a bit wilder. It's common to see motors ranging from 250W all the way up to 750W, and some off-road monsters even push 1,000W or more.
So, what does that mean for your actual speed? While a bigger motor won't just ignore the legal speed limit, it massively changes how the bike feels. A 750W motor will rocket you up to that 28 mph limit way faster than a 250W motor will get you to 15.5 mph. It’s also the muscle you need to haul yourself up steep hills or carry a heavy load without feeling like you're doing all the work.
Torque (The Secret Sauce of Acceleration)
Okay, so watts tell you about the motor's overall strength, but torque is all about its "get-up-and-go." Measured in Newton-meters (Nm), torque is the rotational force that gets you moving. It's that thrilling surge you feel from a dead stop.
Think about trying to open a really stubborn jar lid—that initial twisting force you apply? That’s torque. An e-bike with high torque feels snappy and responsive, which is a game-changer when you're starting on a hill or need a quick boost.
- Low Torque (30-50 Nm): You'll find this on lightweight commuter bikes. It's perfect for flat ground and gives you a smooth, gentle assist.
- High Torque (80+ Nm): This is the stuff of electric mountain bikes and performance-focused bikes. It delivers a powerful kick for scaling steep climbs and accelerating hard.
A high-torque bike makes a world of difference in the city. It gives you the confidence to pull away from traffic lights quickly and merge without getting left in the dust.
Battery Voltage (The Power Source)
If the motor is the engine, then the battery is both the fuel tank and the fuel pump. Battery voltage (V) is a huge piece of this puzzle. You can think of voltage as the "pressure" pushing electricity from the battery to the motor.
A higher voltage system can deliver that power more efficiently. Most e-bikes run on a 36V or 48V battery, though some high-performance models crank it up to 52V or more. Why does it matter? A higher voltage helps the motor run cooler and hold its peak performance longer, which is critical for maintaining speed on a long ride or up a monster hill.
This is the system that works hand-in-hand with the sensors to tell the motor how much of a boost to give you. If you want to get into the nitty-gritty, you can check out our deep dive on the workings of e-bike pedal assist.
At the end of the day, these three components—watts, torque, and voltage—are what define your e-bike’s personality. A bike loaded with a high-wattage motor, tons of torque, and a high-voltage battery is going to feel like a beast that accelerates hard and climbs anything. On the flip side, a bike with more modest specs will give you a gentler, more relaxed ride that's perfect for casual cruising. Understanding these numbers helps you look at a spec sheet and know exactly what you're getting.
What Slows You Down (And Speeds You Up)
The motor might get all the credit, but it's just one part of the speed equation. Think of it as the engine in a car—powerful, sure, but the final speed depends on everything from the road conditions to how much junk you have in the trunk. The real-world speed you feel on an e-bike is a constant tug-of-war between the power pushing you forward and a dozen little things pushing back.
Every ride is different. From the jacket you wear to the path you take, countless variables come into play. Let's break down what's really going on behind the scenes when you twist the throttle or start to pedal.
You, the Rider: Weight and Aerodynamics
The biggest variable, and the one you can’t exactly leave at home, is you. The total weight the motor has to haul around—you, your gear, that heavy lock, your backpack—makes a huge difference. It's simple physics: more mass requires more energy to get moving and to keep moving, especially when fighting gravity on a hill.
But it’s not just about what you weigh; it’s also about how you’re shaped. The invisible force of aerodynamic drag is constantly trying to slow you down. As you speed up, you have to push more air out of the way, and that air pushes back. A loose, flapping jacket acts like a small parachute, forcing your motor to work harder just to maintain speed compared to a more form-fitting cycling jersey.
Ever wonder why Tour de France cyclists are hunched over so low? They're making themselves as small and slippery as possible to cut through the air. You don't have to go that extreme, but it's the same principle at work.
Where You Ride: Terrain and Surface
Your riding environment is a massive factor. A smooth, flat, freshly paved bike lane is the e-bike equivalent of a drag strip. There’s almost no resistance, so all the motor's power goes directly into making you go faster. You'll hit that top assisted speed without breaking a sweat.
Now, picture a steep hill covered in loose gravel. Suddenly, your motor is fighting a two-front war. It's battling gravity just to keep you from rolling backward, and it's dealing with the added friction from the shifty, uneven surface. Your speed will plummet, and your battery will drain much faster. Even something as simple as a strong headwind can feel like you're riding up a gentle, invisible hill.
Your Bike's Setup: Tires and Gearing
Your tires are your only two points of contact with the ground, and they have a surprisingly large impact on speed. Think of them like shoes: you wouldn't wear clunky hiking boots to run a sprint, right?
- Slick, skinny road tires are the racing flats of the bike world. They have minimal tread, which means very little rolling resistance on pavement. They're all about efficiency and speed.
- Big, knobby mountain bike tires are the hiking boots. That aggressive tread is fantastic for gripping dirt and mud, but on pavement, it creates a ton of friction that just eats up speed and battery life.
Tire pressure is just as important. Under-inflated tires get squishy, creating a larger "contact patch" on the ground. This increases rolling resistance and makes your motor and your legs work way harder. Keeping your tires pumped to the recommended pressure is one of the easiest ways to make your e-bike feel faster.
Finally, don't forget your gears! They are the unsung heroes of speed. Using your gears correctly, in sync with the motor's assistance, is the secret to efficiency. Starting in a low gear from a standstill and shifting up as you gain speed lets the motor operate in its sweet spot, helping you get up to speed faster without torching your battery.
Beyond The Bike Lane: High-Speed E-Bikes and The Thrill Factor

So far, we’ve talked about e-bikes designed to play by the rules on city streets and bike paths. But there’s a whole different breed of e-bike out there, built for one thing: pure, unadulterated speed. These are the superbikes of the electric world, engineered for raw power and adrenaline.
Forget the sensible 250W or 750W motors you see on commuter bikes. We’re now in a league where motors start at a massive 2000W and can climb past an insane 5000W. These machines aren’t for your casual ride to the coffee shop; they're built for the thrill of neck-snapping acceleration and conquering tough off-road terrain.
A World Without Speed Limiters
These high-speed e-bikes exist in a class of their own, blurring the line between a bicycle and a full-blown electric motorcycle. They’re designed specifically for private land, racetracks, or dedicated off-road parks. And this is the crucial part: these bikes are absolutely not legal on public roads in the US or Australia without being properly registered as a motor vehicle.
Taking one of these on the street is like riding an unregistered motorcycle, and it comes with all the same legal and safety headaches. It's best to think of them as specialized tools for a very specific job: delivering mind-blowing performance far away from traffic.
These e-bikes are built with a single-minded purpose: to shatter the boundaries of speed and power. They swap everyday practicality for the exhilarating rush of extreme performance, giving us a peek into what the future of electric mobility can look like.
The speeds these bikes can hit are just staggering. A Class 3 e-bike in the US taps out at 28 mph, but these unrestricted beasts leave that speed in the dust. A 3000W e-bike can easily hit 50-60 mph (80-97 km/h), and some of the most extreme models can even break the 90 mph (145 km/h) barrier.
Power, Speed, and Performance
It's a simple and thrilling equation: more power equals more speed. As the motor wattage goes up, so does the velocity. The fastest electric bikes on the market show just how far the technology has come, with top-tier models hitting speeds between 50 and 93 mph thanks to motors ranging from 2000W to over 5000W.
The correlation is pretty consistent:
- 1500W Motors: You're looking at speeds around 35-40 mph.
- 2000W Motors: These can push you into the 50-65 mph range.
- 3000W Motors: Speeds often rocket past 70 mph.
This kind of performance is a testament to the incredible advances in electric motor and battery tech. If you're curious about the nitty-gritty of how engineers are pushing these limits, you can find some fascinating details on how fast e-bikes can go.
For those who are truly obsessed with getting every last bit of performance out of their ride, it can be helpful to look at speed optimization in other electric vehicles. The principles of power, aerodynamics, and efficiency often carry over. You can find more tips and performance insights for optimizing electric vehicle speed that might spark some ideas. These superbikes show us the bleeding edge of what's possible, but they also highlight the amazing engineering required to balance power with safety and control.
Finding The Right Balance Between Speed, Safety, And Range
Let's be honest, hitting a high speed on an e-bike is a blast. That rush is a huge part of the fun. But like most things in life, it’s all about balance. The real secret to a great ride isn't just about pinning the throttle; it's about finding that sweet spot between speed, staying safe, and making sure your battery doesn't die halfway through your adventure.
Think of it like driving your car on the highway. Floor it, and you can practically watch the fuel gauge drop. Your e-bike battery works the exact same way. Riding constantly at top speed in the highest assist mode is like a workout for your battery—it's going to get drained, and fast.
Maximizing Your Miles Per Charge
If you want to squeeze every last mile out of a single charge, a few tweaks to how you ride can make a massive difference. It’s all about riding smarter, not harder.
Here are a few simple habits that will keep you rolling longer:
- Be Smart with Assist Levels: Resist the urge to live in "Turbo" mode. Start out on a lower assist level for flat stretches and save the high-power modes for when you really need them, like tackling a steep hill or getting a jump on traffic.
- Ease Into It: Quick, jerky starts from a dead stop are a huge power suck. Try to accelerate smoothly and hold a consistent speed.
- Keep Pedaling: Remember, the motor is there to assist you, not do all the work. A steady, consistent pedaling rhythm helps the motor operate much more efficiently and conserves a ton of battery life.
- Check Your Tires: This one's easy to forget. Properly inflated tires roll with far less resistance, which means your motor doesn't have to strain just to keep you moving.
Finding that perfect cruising speed where you're moving along nicely without redlining the motor is the key to a long, enjoyable ride. It's the best way to get home without the dreaded "range anxiety."
For a much deeper dive into what makes your battery tick, check out our guide on everything you need to know about electric bike battery life.
Speed, Safety, and Staying Aware
Going faster doesn't just impact your battery—it completely changes the game when it comes to safety. The faster you're moving, the less time you have to react to the unexpected, and the more serious the outcome of a fall or collision can be.
The single biggest thing to remember is that your stopping distance grows exponentially. Doubling your speed from 10 mph to 20 mph doesn't just double the distance it takes to stop; it can actually quadruple it. This means you need to be scanning much farther down the road and anticipating what cars, pedestrians, and other cyclists are going to do long before you get to them.
Higher speeds also call for better gear. A standard helmet is fine for a casual park ride, but if you're regularly hitting 28 mph on a Class 3 e-bike, you should really think about upgrading to a helmet with a higher safety rating—something closer to what you’d wear on a moped. It's all about matching your gear to your speed. Ultimately, a great ride happens when you blend the thrill of speed with a healthy respect for safety and efficiency.
Got Questions About E-Bike Speed? We've Got Answers.
Alright, we've covered a lot of ground, but you might still have a few things rattling around in your head about how fast these bikes really go. Let's clear up some of the most common questions we hear all the time.
Can I Make My Electric Bike Go Faster?
Look, the short answer is yes, but it's a can of worms you might not want to open. This is often called "de-restricting" or "unlocking," and it involves tinkering with the bike's software or hardware to bypass the built-in speed limiter. Sure, it can make the bike faster, but the trade-offs are pretty steep.
For starters, you can kiss your warranty goodbye. More importantly, a de-restricted e-bike is no longer street-legal in Australia or most of the US. You’re also putting a ton of extra stress on the motor and battery, which can seriously shorten their lifespan. Honestly, for your own safety and to stay on the right side of the law, it’s best to stick with the bike’s factory settings.
Is A 750W Motor Faster Than A 250W Motor?
This is a fantastic question because the answer isn't as simple as it seems. If we're talking about the legally assisted top speed, then yes. A 250W bike in Australia is limited to 25 km/h of motor assistance, whereas a 750W Class 3 bike in the US can assist you up to 28 mph.
But the real story is about how you get to that speed. The 750W motor delivers a whole lot more punch. It's all about acceleration and torque—it'll get you up to speed in a flash, power up steep hills like they're nothing, and won't flinch if you're hauling a heavy load.
Think of it like this: a small hatchback and a big SUV are both driving in a 30 mph zone. The SUV's powerful engine gives it the muscle to get up to speed effortlessly and handle tough terrain. That's the difference you feel with a 750W motor.
How Does Pedal Assist Affect My Speed?
Pedal assist is the secret sauce of an e-bike. It’s a clever system that knows when you’re pedaling and kicks in the motor to give you a boost. You can usually choose from a few different levels, often called something like "Eco," "Tour," or "Turbo."
Here’s a quick breakdown of what that feels like:
- Eco Mode: You get a gentle nudge from the motor. It feels like you've suddenly got a tailwind, making pedaling easier while sipping on battery power. It's perfect for long, flat rides.
- Turbo Mode: This is full-power mode. The motor gives you everything it's got, rocketing you up to the bike's top assisted speed with barely any effort.
Your actual speed is a team effort between the motor's push (up to its legal cutoff) and your own pedaling. You can always pedal faster than the motor's limit, but at that point, any extra speed is 100% powered by you.
Ready to find the perfect ride that blends speed, style, and pure fun for your commute or weekend trails? At Punk Ride LLC, we’ve got a massive lineup of top-notch electric bikes and scooters from the best brands out there. Stop dreaming and start riding.




Share:
Electric Scooter Dual Motor: The Ultimate Explainer
Folding electric bike for commuters: The Ultimate City Guide